The fundamental thermodynamic relation
First Law
If particle number is not held constant:
Example: Ideal gas (assuming fixed N)
S is entropy? yes!
Where are arbitrary
Often Needed:
and
This approximation works only at high temp and low density. Falls apart at low temps.
Gibbs - Duharm Relation
Maximum at fixed E,V,N
If you double the size of the system , you will ideally have double the entropy.
Extensive State Function: (?)
is the size of the system?
extensibility?
Then set
Compare with first law:
This is the Gibbs-Duham relation
The third law of thermodynamics
(With exceptions)
Quasi-static case:
@ constant volume
The heat capacity isn’t always a constant, it may depend on temperature.
Similarly, you can repeat the same for constant pressure P
Generalized Thermodynamic Potentials
Equilibrium with Gradients
System small compared to a large reservoir.
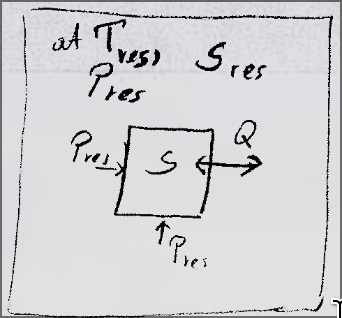
Subcase: Hemholtz Free energy
- Fixed volume
Maxwell Relation and Applications
Why does this Maxwell dude do literally everything